Exercise, Depression, and the Brain
Whether you're experiencing a simple case of the Monday blues or more persistent symptoms of depression, exercise can help boost your mood.
Getting regular exercise is important for good physical and mental health. Exercise can help stimulate parts of your brain that aren't as responsive when you're feeling depressed. It also promotes the release of feel-good brain chemicals. It may also help distract you from your worries and improve your confidence.
Exercise and brain chemistry
Depression is a mood disorder that causes persistent feelings of apathy and sadness. It's a complex condition, with several contributing factors. Changes in your brain biochemistry likely play a part.
'Simply put, most people who are depressed have something wrong with their brain chemistry," says William Walsh, Ph.D., president of the Walsh Research Institute, a nonprofit mental health research institution in Illinois. 'Life experiences can make things worse,' he adds, 'but usually the dominant problem is chemistry."
Exercise can help relieve symptoms of depression in several ways. Among other benefits, it helps stimulate the release of feel-good brain chemicals.
Endorphins and other neurotransmitters
The first thing you might think of when it comes to exercise and depression is what is commonly known as 'runner's high.' This describes the release of endorphins that your brain experiences when you physically exert yourself. Endorphins are a type of neurotransmitter, or chemical messenger. They help relieve pain and stress.
Endorphins are only one of many neurotransmitters released when you exercise. Physical activity also stimulates the release of dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin. These brain chemicals play an important part in regulating your mood.
For example, regular exercise can positively impact serotonin levels in your brain. Raising your levels of serotonin boosts your mood and overall sense of well-being. It can also help improve your appetite and sleep cycles, which are often negatively affected by depression.
Regular exercise also helps balance your body's level of stress hormones, such as adrenaline. Adrenaline plays a crucial role in your fight-or-flight response, but too much of it can damage your health.
Other mental health benefits of exercise
Exercise can have other mental health benefits too. For example, focusing on your body's movements during exercise may help distract you from upsetting thoughts. Setting and meeting exercise-related goals may also boost your confidence and sense of control.
When you exercise with other people, it can provide mood-boosting social benefits. For example, consider walking in the park, taking a yoga class, or joining a recreational sport team with a friend or family member. Exercise classes can also be a good place to meet new people. You can enjoy the physical stimulation of a workout, while getting social stimulation too.
Developing an exercise routine
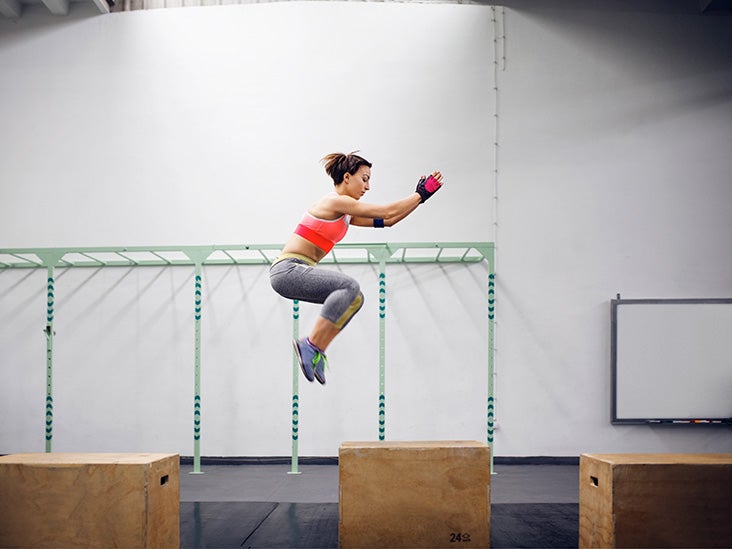
While any amount of exercise can help relieve the symptoms of depression, regular exercise is best. Some types of exercise may be more beneficial than others.
Aerobic workouts are most associated with positive results in treating depression. Aerobic exercise elevates your heart rate, which improves circulation in your brain. This helps promote healthy brain function and balanced brain chemistry. Aerobic exercise also provides many physical health benefits.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention encourage most adults to get at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week. You can reach this goal by taking a brisk 30-minute walk around your neighborhood, five days a week. Other examples of aerobic activity include swimming, bicycling, and playing basketball.
You should also schedule at least two sessions of muscle-strengthening activities per week. Weightlifting, yoga, and Pilates are examples of activities that strengthen your muscles.
Eating a healthy diet
Eating a well-balanced diet is also important for good mental health. For example, complex carbohydrates and protein-rich foods can help improve your mood and concentration. They also provide the energy and nutrients needed to fuel your workouts.
For a nutritious diet, eat a variety of vegetables, fruits, whole grains, low-fat dairy products, and lean proteins. Don't eat a lot of foods that are high in refined sugar, saturated fats, or salt. Only drink alcohol in moderation.
The takeaway
A range of factors can contribute to depression. Your brain chemistry is an important one. In many cases, you can improve your brain chemistry with something as simple as regular exercise. Getting 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity per week is an important part of staying healthy. It can boost your mood and energy, while strengthening your muscles, lungs, and heart.
If you suspect you have depression, speak to your doctor. They may recommend a variety of lifestyle changes, including changes to your exercise routine. They may also prescribe other treatments, such as medications, therapy, or a combination of both.
-
 6 interesting genetic traits that children will inherit from their parents
6 interesting genetic traits that children will inherit from their parents
-
 7 effects of asparagus on child development
7 effects of asparagus on child development
-
 Does cutting blood hair for babies bring good luck?
Does cutting blood hair for babies bring good luck?
-
 The more babies eat, the higher the height they develop, especially the second kind
The more babies eat, the higher the height they develop, especially the second kind
-
 Children with chicken pox should eat to quickly recover from the disease, without leaving a deep scar?
Children with chicken pox should eat to quickly recover from the disease, without leaving a deep scar?
-
 The more food is cooked, the better it can be for health, especially the second type
The more food is cooked, the better it can be for health, especially the second type